Control System
this article discusses and represents the Definitions, examples, types, configuration, and optimization of control systems. |
| Industrial Control System |
What is the control system?
The control system is a group of electrical, hydraulic, Automation, pneumatic, and mechanical systems that are configured together to supervise and manage the performance of a process to achieve the optimum output of the process.A control system could be a small module for controlling one process or could be widely in industrial processes where multiple tasks and objectives are controlled. Each control signal in the control system is called a control loop. The size of the control system used is determined based on the process and the number of loops used in it.
What is the control system example?
An easy and simple example of the control system is the temperature control loop. This example can be found in your home in air conditioners, cookers, heaters,..etc where you enter the temperature setpoint by the air condition remote control or the front buttons of the cooker or microwave and the device works to achieve the temperature and keeps it at its desired value.What are the types of control systems?
Types of control systems are:
- Open-loop control system
- Closed-loop control system
- Linear control system
- Non-linear control system.
- Analogue control system
- Digital control system
- SISO (single input – single output) control system
- MIMO (multi-input – multi-output) control system
- Discreet control system
- Continuous control system.
- Time variant control system.
- Time invariant control system.
Generally, the open and closed-loop control systems are the main control systems and can represent the other types of control systems.
What is the open loop control system?
 |
| Open loop Control |
The advantages of the open loop are that it is simple not complicated, low or free maintenance needed because of its simplicity, and finally, it is economically widely used. The disadvantage of this type is that you will never get the exact value you request. All time the output temperature will be up and down for the previous example. It is not reliable, has very slow performance, and cannot be optimized.
What is the closed-loop control system?
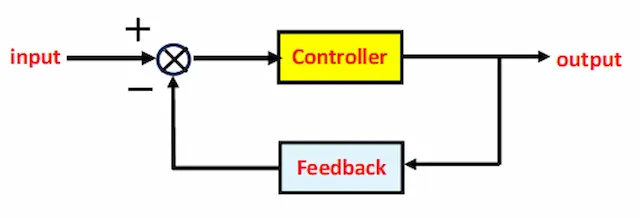 |
| Closed Loop Control |
The advantages of the closed-loop control are that it is very fast, and can deal with many parameters at the same time, and the important one is that the closed-loop control over the open-loop control is that you will get exact, accurate, and stable output of the process. The closed loop has also some disadvantages like it is complicated and has a high initial cost.
The control system normally consists of multiple stages cascaded together. The equipment in each stage is different from the other stage and according to the process itself but the common modules are:
What is the complete configuration of the control system?
 |
| Complete Control Loop |
- The input module is where the setpoint/reference is set by entering the required value. The input tools for the data entry could be hardware like a potentiometer or digital through a computer
- Comparator module, where the preset value is compared with the actual value. The output of the comparator is called the error or deviation value.
- The controller module takes the error signal from the comparator. The output of the controller is called the control signal which is calculated based on the controller configuration. It could be analogue value, digital value, or pulse depending on the process element.
- Process element: it could be a heater, actuators, motor … etc. The function of this process element is to convert the control signal which is an electrical signal to a physical quantity like temperature, movement, start/stop, and rotation.
- Feedback module: This includes the instrumentation system part of the control system module.
What is the optimization in the control system?
The control system can be supported by a special computerized system to optimize the output of the control system. When the optimizer is added to the control system many advantages and benefits will be added to the system. These benefits are represented as follows:- System stability by minimizing the oscillation of the output around the reference value.
- Minimizing the oscillation of the output around the reference value leads to minimizing the error and deviation from the set point which makes the system output more accurate.
- The success of achieving the previous 2 points enables to increase in the production rate at the same values of inputs. In some cases, could reach a 5% production increase.
- The result of all these items finally lowers the cost which is the main task for all systems and companies looking for.
