Gas Flow Management in Industrial Systems
In the previous article, we discussed the gas valve train and its role in the industrial processes that have burners. We discussed also its key equipment. In this article, we will explore and explain the operation of the gas train valve to achieve the maximum performance of the burner and make its operation efficient and safe to get the desired temperature. |
| Configuration and PID controllers |
A special PLC program in the main automation system operates the gas train valve based on the objective of the main process needs burner. The PLC hardware reads the signals from the instrumentations that are installed on the gas train such as pressure and temperature sensors and the limit switches that show the position of each shut-off valve.
 |
| Gas train valve unit |
Before starting the gas train valve:
- The main gas pressure gauge reads the line pressure at the upstream part. The high-pressure switch HPS (5)’s signal should be healthy according to the adjusted setting to protect the valve train from excessive high pressure. The manual valves (7), (10), and (14) are open. The manual valve (11) is closed. The pressure control valve works automatically to keep the pressure at the desired value.
- The two shut-off valves (9) and (15) are closed. a vent shut-off valve (13) is opened. The flow meter’s reading (12) is zero and the gas control valve (16) is at its minimum position. The minimum position setpoint of the gas control valve is the controller position that enables a minimum gas flow to make the burner flame on.
- As the system is not started yet and there is no gas in the pipes the LPS pressure switch (17) is faulty and will turn healthy after starting the gas train valve. All these conditions should be confirmed before starting the gas train valve.
- Based on the automation system used, the gas valve train is a group of devices working together to perform the objectives of the gas valve train. The operator starts the gas valve train separately as a stand-alone group or the group is automatically started in a sequence for multiple groups.
- When the gas valve train started, the shut-off valves (9) and (15) opened, the vent shut-off valve (13) closed, and gas passed through the pipe within a minimum flow rate measured on the gas flow meter. The gas flow is according to the minimum position of the gas flow control valve.
What is the ignitor and what is its role in starting burners?
- The ignitor is the device that provides and generates the spark needed to ignite the air-gas mix. The ignitor is normally installed in the burner at the downstream part of the gas valve train. Once the gas flows and reaches the burner, the ignitor is activated and ignites the gas-air mixture starting the combustion process.
- The ignitor is equipped with a flame sensor or a flame detector to scan whether the flame is on or not. Suppose the flame is not on within a predetermined time in the main program. The program gives the order to shut down the gas valve train as a safety interlock to prevent gas accumulation inside the burning zone.
- The ignitor uses an electrical discharge process where rapidly discharging electrical energy across a small gap creates sparks. It is powered by an electrical source. The Ignitor uses an electronic ignition module or a step-up transformer to significantly increase the voltage (thousands of volts). The voltage could be DC or AC voltage.
- This high voltage breaks the dielectric strength (resistance) of the air gap between the two ignitor’s electrodes to produce a spark. When the flame is on and stable, the gas flow can be controlled manually or automatically through the Gas flow controller (normally it is a PID controller) to get the desired temperature which is the target of the process.
What are the gas flow control operation modes?
1- Manual Mode.
In manual mode, the operator increases or decreases the flow by changing (increasing or decreasing) the position (percentage) of the gas control valve. But in this process, the result is inaccurate where the gas flow’s reading oscillates based on the control valve’s position leading to instability of the output temperature.2- Semi-Automatic mode.
In this case, the operator enters the value of the desired gas flow as a set point to the controller and changes it according to a well-known curve for the temperature and gas flow. The controller increases or decreases the gas control valve’s position automatically till reaching the exact required gas flow without considering the temperature.3- Full-automatic control mode.
This mode works to control the required temperature, not the gas flow. The operator enters the temperature’s set point and the controller compares the signal from the temperature sensor and the set point. Based on the difference between the set point and the actual, the order is sent from the controller to the gas control valve by opening or closing till the preset temperature. This is more accurate than controlling the flow.Controlling the operation of the gas valve unit
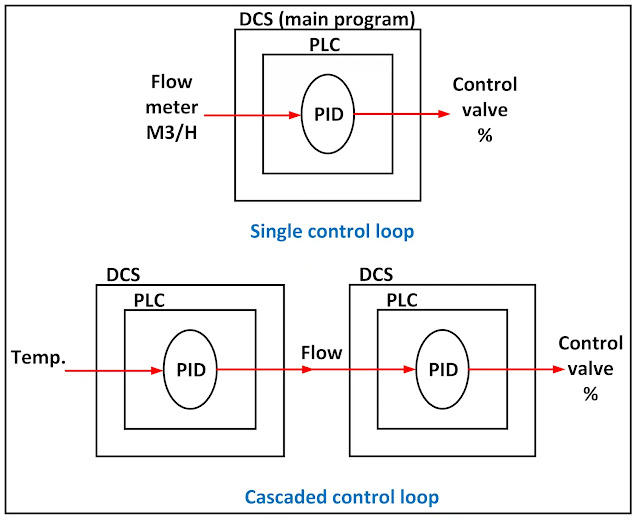
- As per the configuration figure, The control process could be done by one PID control to control the gas flow. It could also use one PID controller to control the output temperature. it is better to have two cascaded PID controllers to get the maximum efficiency and accuracy of the system (gas train valve, burner, and control system).
- One for the temperature and its output is the gas flow which is an input to the second PID controller. The output of the second PID controller goes to the gas control valve to open and close according to the needed flow based on the first PID controller’s temperature set point.
- The control program stops the gas valve train group If a safety issue is detected for the gas pressure or any device has a malfunction or unaccepted error, by closing the 2 shut-off valves (9) and (15) and opening the vent shut-off valve to release the pressure. The following figure explains the stand-alone controller for only the flow controller and the cascaded control which is better than the first controller.
Maintenance note:
The flow meter (12) can be maintained or changed during the operation of the gas train valve by closing manual valves (10) and (14) and opening the manual valve (11) under the condition of putting the PID controller to manual mode to fix the position of the gas control valve.
Safety note:
The main manual valve (7) should be closed for any maintenance activities in the gas train valve. When the gas valve train unit stops for a long time, it is better to close all manual valves for safety.












No comments:
Post a Comment